Building Awareness of the Link between Fistula and Gender-Based Violence
Genital fistula, an abnormal hole between the vagina and rectum or bladder that causes urinary or fecal incontinence, is a devastating, preventable condition that no woman should have to endure. It usually results from inadequately managed, prolonged or obstructed labor, surgical error, or trauma [1, 2]. Although rare, it can be completely debilitating—physically, socially, and economically—particularly to women who live in remote areas without access to treatment; women with fistula are often shunned from the household or society, which can cause immense suffering [3].
While sexual violence can cause traumatic fistula, the vulnerable state of women with fistula gives reason to suspect that the risk of violence could also increase after the onset of fistula [4, 5, 6], though no studies have attempted to evaluate this to date. Moreover, because it is so rare, it is difficult to capture statistically significant associations with the condition.
The DHS Program provides an opportunity to study such rare events because of the inclusion of standardized questions in numerous, nationally-representative surveys with large sample sizes. In a study conducted to further examine the relationship between fistula and violence, data were pooled from 12 DHS surveys, 11 conducted in Sub-Saharan African countries and one in Haiti, where standardized modules (sets of questions) on the two topics were included.
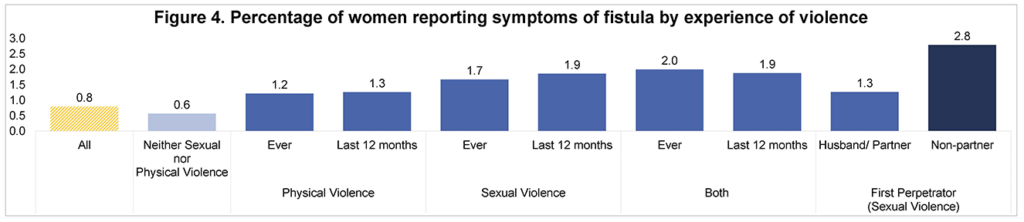
In total, 90,276 women were included in the analysis. Among these women, the prevalence of self-reported symptoms of fistula ranged from 0.4% to 2.0%. Regression analyses confirmed an association with sexual violence: women who have experienced sexual violence, both ever as well as within the 12 months preceding the survey, have almost twice the odds of reporting symptoms of fistula. Although there are no questions posed on timing of onset of symptoms of fistula in the DHS, the association with lifetime as well as recent experience of sexual violence suggests that violence could occur both before as well as after fistula’s onset.
One other finding of interest was that women whose first experience of sexual violence was committed by a non-partner had over four times the odds of reporting symptoms of fistula than women who did not report sexual violence. Although inferences from these findings can only be made with caution, the temporality relationship between fistula and sexual violence deserves further investigation.
In light of International Day to End Fistula on May 23, it is imperative to continue to work towards minimizing occurrence of fistula by building awareness around conditions that contribute to and result from this morbidity. This study shows yet another disheartening correlation between gender-based violence and poor health outcomes for women. It provides even more impetus for training and sensitivity for women’s health care providers in this area.
 A poster presentation of the study was exhibited at the 2016 Annual Meeting of the Population Association of America (PAA) in Washington DC. More information can be found in this poster.
A poster presentation of the study was exhibited at the 2016 Annual Meeting of the Population Association of America (PAA) in Washington DC. More information can be found in this poster.
- Longombe AO, Claude KM, Ruminjo J. Fistula and traumatic genital injury from sexual violence in a conflict setting in Eastern Congo: case studies. Reprod Health Matters. 2008 May;16(31):132-41
- Raassen TJ, Ngongo CJ, Mahendeka MM. Iatrogenic genitourinary fistula: an 18-year retrospective review of 805 injuries. Int Urogynecol J. 2014 Dec;25(12):1699-706.
- Baloch, B.A., A. Salam, D. ZaibUnnisa, and H. Nawaz. 2014. Vesico-Vaginal Fistulae. The Professional Medical Journal, 21(5), 851-855.
- ACQUIRE. 2006. Traumatic gynecologic fistula: A Consequence of Sexual Violence in Conflict Settings. A report of a meeting held in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, September 6-8, 2005. New York, The ACQUIRE Project/EngenderHealth.
- Peterman A, Johnson K. Incontinence and trauma: sexual violence, female genital cutting and proxy measures of gynecological fistula. Soc Sci Med. 2009 Mar;68(5):971-9.
- Naved RT, Blum LS, Chowdhury S, Khan R, Bilkis S, Koblinsky M. Violence against women with chronic maternal disabilities in rural Bangladesh. J Health Popul Nutr. 2012 Jun;30(2):181-92.




Hi Lindsay,
I came across your site and really like your mission. My team and I are currently preparing a Female Genital Mutilation guide in order to raise awareness and offer guidance in case of need.
I would love your feedback on the guide as well as your idea to spread the word.
You can contact me directly on tim@junomedical.com.
Best from Berlin
Tim
Thank you for your inquiry. While the study described in this blog did not explicitly examine the association between female genital cutting and self-reported symptoms of fistula, I have examined the bivariate relationship between the two in previous work, where a relationship was not found in a majority of countries studied. However, this result was not supported by other research. You can access this study and find references to FGM and fistula here: The Supplement to DHS Analytical Studies 17 (http://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/OD67/OD67.pdf).