World Breastfeeding Week 2020

Countless studies have shown that breast milk is beneficial to an infant’s growth and development during the first year of life. This year’s theme for World Breastfeeding Week from the WHO and World Alliance for Breastfeeding Action highlights the importance of supporting breastfeeding with skilled breastfeeding counseling.
The DHS Program has collected data for more than 30 years about initial breastfeeding, breastfeeding status and frequency, and the median duration of breastfeeding. Additionally, the Service Provision Assessment (SPA) provides insight on the overall readiness of health facilities to promote and support early breastfeeding as part of the antenatal care and newborn services package. Putting the baby to the breast within one hour of birth ensures that the infant receives the colostrum or “first milk” which contains antibodies to protect against infectious diseases and lipids to promote weight gain. Choosing to breastfeed exclusively for at least six months provides natural, renewable, and free food that does not require preparation or packaging.
In 2019, The DHS Program authored a study, Examining the Role of Health Facilities in Supporting Early Breastfeeding in Haiti and Malawi, about the relationship between the breastfeeding-related health service environment during antenatal care (ANC) and early initiation of breastfeeding. Using data from recent SPA surveys in Haiti and Malawi, three variables related to the health service environment are defined: availability of facilities with ANC services that report routine counseling on breastfeeding, provider training on breastfeeding, and observation of breastfeeding counseling during ANC and client’s report of breastfeeding counseling.

In Haiti, nearly all ANC facilities in both urban and rural areas report routine breastfeeding counseling during ANC, while 29% of urban and 26% of rural ANC providers received recent training in breastfeeding or infant and young child feeding (IYCF). Among urban and rural clients, 4% received counseling on breastfeeding.
The results of the analysis show that over 95% of facilities in both urban and rural areas of Haiti and Malawi report that breastfeeding counseling is provided. However, 26% to 40% of providers have received training in counseling on breastfeeding in the two years before the surveys, and only 4% to 10% of clients have received counseling. Analysis of linked SPA and DHS data show that having more providers recently trained on breastfeeding is significantly associated with increased odds of early breastfeeding among ANC clients in urban areas of Haiti and Malawi.
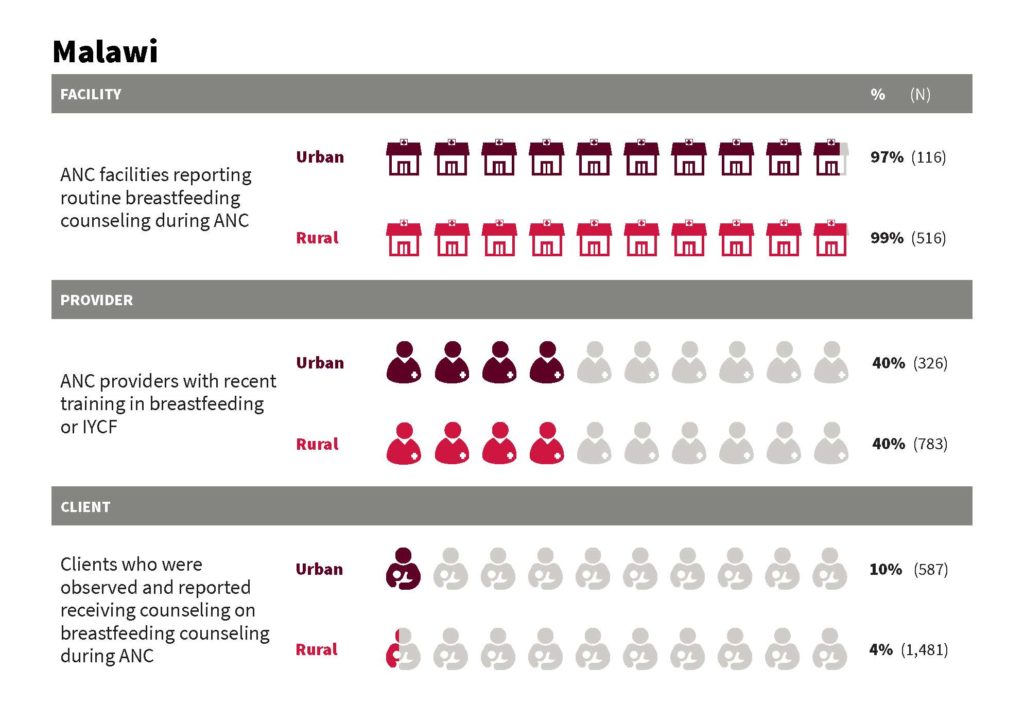
In Malawi, nearly all ANC facilities in both urban and rural areas report routine breastfeeding counseling during ANC, while 40% of both urban and rural ANC providers received recent training in breastfeeding or IYCF. Only 10% of urban clients and 4% of rural clients received counseling on breastfeeding.
This study clearly defines the role health institutions can play in promoting breastfeeding by providing support and education to new mothers and their families. By doing so health institutions can enable mothers to exclusively breastfeed for the first six months of life to ensure optimal growth, health, and development.
Featured image: © 2007 Virginia Lamprecht, Courtesy of Photoshare
