DHS Data Support Breastfeeding among Working Parents

Breastfeeding provides a range of benefits to children and their mothers. Benefits of breastfeeding include protecting children from disease, supporting their healthy growth and development, and reducing the risk of some cancers for mothers. Protecting, promoting, and supporting breastfeeding requires data to inform and drive action. The first week of August is World Breastfeeding Week. This year’s theme is Enabling breastfeeding: making a difference for working parents. DHS Program surveys collect data on several breastfeeding indicators and background characteristics such as employment status relevant to working parents. Data users can better understand breastfeeding practices in a country with indicators collected in DHS surveys such as:
Indicator | Definition | Why it matters |
Children ever breastfed  | Percent of children age 0-23 months who were ever breastfed | This indicator reflects the cultural acceptance of breastfeeding. |
Early initiation of breastfeeding  | Percent of children age 0-23 months who were put to the breast within 1 hour of birth | Breastfeeding within the first hour after birth provides a range of benefits including protecting the newborn from disease. |
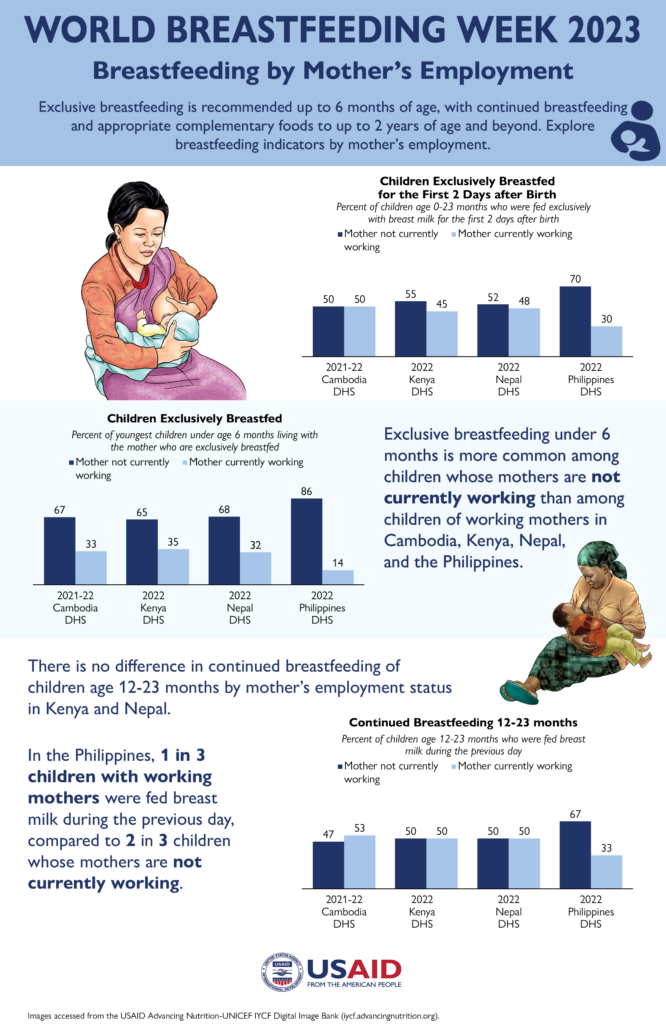
Children exclusively breastfed for the first 2 days  | Percent of children age 0-23 months who were fed exclusively with breast milk for the first 2 days after birth | Feeding newborns anything other than breast milk in the first 2 days after birth can delay early initiation of breastfeeding and interrupts exclusive breastfeeding. |
Exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months  | Percent of children age 0-5 months who were fed exclusively with breast milk during the previous day | Breast milk is sufficient to provide all the nutrients and liquid an infant requires for optimal growth and development. Exclusive breastfeeding also lowers the risk of infections such as diarrhea and respiratory illnesses in children and protects against child overweight and obesity. |
Continued breastfeeding 12-23 months  | Percent of children age 12-23 months who were fed breast milk during the previous day | Breastfeeding until age 2 and beyond supports children's growth and development. |
Explore children ever breastfed, early initiation of breastfeeding, and exclusive breastfeeding under 6 months using STATcompiler.
Breastfeeding counseling and observations by health care workers have a positive impact on breastfeeding practices. In many countries, mothers are observed during postnatal care to help with correct positioning and latch of the infant at the breast. New indicators in DHS-8 to better understand breastfeeding counseling include:
Indicator | Definition | Why it matters |
Breastfeeding counseling during pregnancy  | Percent of women age 15-49 with a live birth or stillbirth in the last 2 years who received counseling about breastfeeding during pregnancy of the most recent live birth or stillbirth from a health care provider | Breastfeeding counseling during the antenatal period has a positive impact on early breastfeeding. |
Breastfeeding counseling during postnatal care  | Percent of most recent live births in the last 2 years for whom the mother was counseled about breastfeeding by a health care provider during the first 2 days after birth | Breastfeeding counseling during the postpartum period has a positive impact on exclusive breastfeeding. |
Direct observation of breastfeeding during postnatal care  | Percent of most recent live births in the last 2 years for whom the mother was observed breastfeeding by a health care provider during the first 2 days after birth | Direct observation of breastfeeding supports mothers to ensure correct positioning and latch of the infant at the breast for successful milk transfer. |
Breastfeeding counseling indicators will soon be added to STATcompiler.
Breastfeeding indicators are also collected in Survey Provision Assessments (SPA). The DHS Program’s revised SPA assesses health facilities to provide an overview of a country’s health service delivery with a focus on quality of care. Health facilities support breastfeeding by ensuring they have trained staff available to provide breastfeeding counseling during antenatal and postnatal care, by not promoting breastfeeding substitutes, and by linking mothers to breastfeeding support available in the community. The revised SPA includes 19 breastfeeding indicators, including 12 that are new or revised. These indicators can be used to track the Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative Ten Steps to Successful Breastfeeding. To learn more, review the revised SPA questionnaires (especially the health worker, antenatal care and postnatal care questionnaires).
Explore breastfeeding by mother’s employment status from recent DHS-8 surveys in the infographic below. This infographic was created from a cross tabulation of women who worked in the last 12 months and are currently working and breastfeeding indicators. DHS Program data users can access The DHS Program’s Code Share Library on GitHub to copy or download DHS-8 code for breastfeeding indicators for Stata, SPSS, and R.
Feature image and other images accessed from the USAID Advancing Nutrition-UNICEF IYCF Digital Image Bank (iycf.advancingnutrition.org).